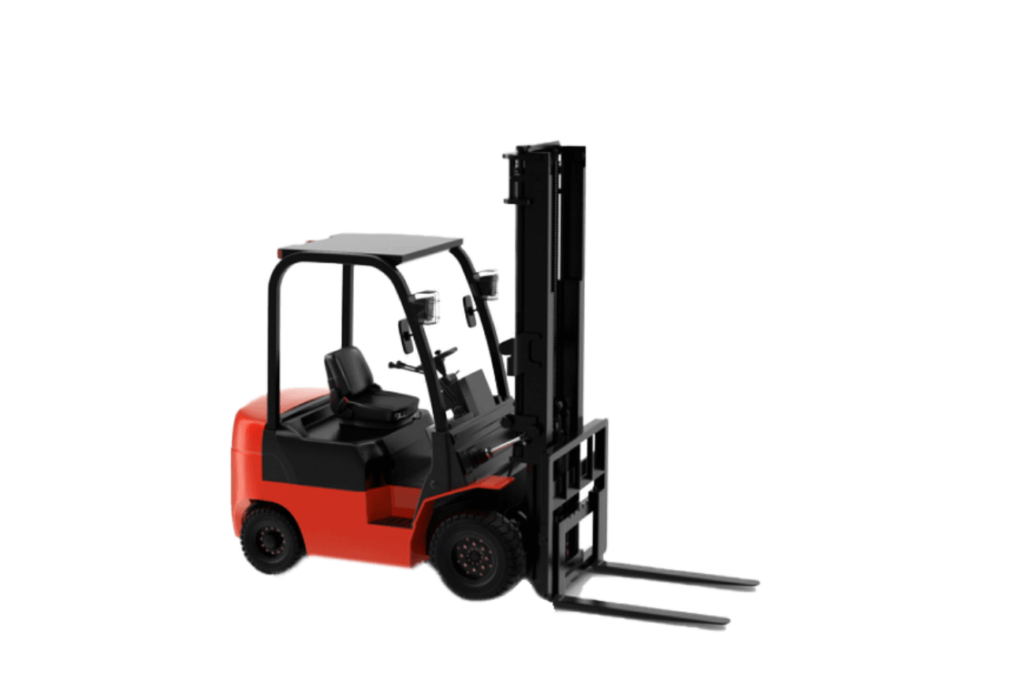
Forklifts are machines for lifting and transporting materials of large size, weight and / or volume. This machine is frequently used in industries with areas or spaces for storage and loading of materials, such as construction materials companies and warehouses of large shopping centers.
Its primary function is to lift, lower, and move loads with little or no manual effort. This is possible by using a mast on the front of a forklift.
It is defined as a mobile counterweight equipment, since the load it handles is outside the distance between its axes. Counterbalanced forklifts are based on the principles of balance and stability. The balance point is located on the centerline of the drive shaft.
Every single
part of the forklift is designed to fulfill a function, it offers solutions for
the handling of loading and unloading always taking into account the demand of
work to be executed, but to carry out the execution efficiently, the parts of
this machine must be known to help to decide with more certainty what will be
done with the forklift.
Forklifts parts
The fundamental parts of a forklift are:
Truck Frame is considered one of the most vital components which forms the base of the machine. All of the key components of the forklift including wheels, counterweight and mast are attached to the truck frame.
The frame is generally made of two channel sections of alloy steel with a standardized width of 86 cm (34 inches) overall. Semi trailers and tank trailers in many instances now employ the integral, or unitized, type of construction.
The chassis of these machines is only supported at an intermediate point of the rear axle. It is a triangular chassis (2 supports on the front axle and 1 support on the rear axle).
Since it only has an intermediate fulcrum on the rear axle, this machine is unstable and great care must be taken when handling it, especially not to make sharp turns.
It has two long extensions(like arms) that are located longitudinally, horizontally and parallel to each other, which will allow us to load underneath precisely between the free spaces of the pallets.
The forklift mast is the raised vertical support that allows loads to raise and lower. For most forklifts, the mast was designed toward the front of a forklift and directly in the forklift operator’s line of sight.
Forklift masts come with various sections that raise or lower the forklift carriage along with the forks. These include:
When you’re gonna select a forklift, it is important you know the various characteristics and terminology of a forklift mast: the mast lift height, the free lift height, and the extended height and the lowered height. This will allow you to select a forklift that is designed to meet the specific needs of your applications.

The forklift lift cylinder powers the vertical movement of the mast, or the raising and lowering of the forklift truck and forks. The lift cylinder is generally hydraulically powered and is a single acting hydraulic cylinder, meaning that it pushes in one direction.
Similar to the lift cylinder, the tilt cylinder controls movement for operating purposes. The key difference is that the tilt cylinder controls the tilt movement of the carriage and the angle of the forks relative to the ground.
The counterweight is the weight installed on the forklift to help offset the weight being lifted by the forklift. This helps keep the forklift stable during lifting and lowering operations. The forklifts were designed with maximum transport capacities using the counterweight for balancing, so it is important to know the intended transport capacity for the forklift. Check the rating plate on the forklift for this information.
Internal combustion forklift counterweights are located toward the rear of the forklift or on the opposite side of the forks. For electric forklifts, the battery acts as a counterweight.
This platform is located in front of the forklift mast, which is used to mount objects to be controlled through the mast. This includes forklift forks, load backrest, and other features of a forklift that come into direct contact with loads.
The forklift cabin can be open or closed depending on the options chosen. It is the space where the forklift operator controls and operates the equipment. The cab contains a variety of forklift operating controls and components, and features that are used to maneuver and manipulate the forklift. This includes, but is not limited to: Brake pedals, steering wheel, mast controls, accelerator pedals, inching pedal, parking brake, levers, and gauges.
All forklifts require tires to operate, but the types of tires and the distribution of tires on the forklift can vary significantly. Forklifts that use four tires are capable of lifting heavy loads and are versatile for many applications. Three-wheel forklifts are ideal for indoor environments where space is limited and the ability to turn and maneuver efficiently is important.
There are two main types of forklift tires:
Solid Tire Tires – Generally used for forklifts that operate indoors, where surfaces are flat, smooth, and consistent. Solid tire tires are generally less expensive and easier to maintain, but lack the traction that pneumatic tires offer. Solid tire rim forklifts are ideal in warehouses and other indoor environments where small turning radii are necessary.
Pneumatic Tires – Pneumatic tire forklifts are generally used to operate outdoors, where surfaces can be uneven, rough, or variable. Pneumatic tires are more similar to the tires on your car making them better on unpaved driving surfaces and rough terrain. Pneumatic tires can be air pneumatic tires, meaning that they are filled with air, or solid pneumatic tires, meaning that they are made entirely of solid rubber.
This could be traction or steering wheels:
Traction Wheels
The drive wheels provide the power needed to move the forklift and are often larger than the steer wheels because they are responsible for carrying a large amount of mass during operation.
Steering Wheels
The steer wheels are generally located at the rear of the forklift and make it easy to steer. It is easier to control the movement of the forklift using the rear wheel (s).
It refers to the forklift’s power supply, which may include a motor or batteries depending on the type of forklift. Forklifts can be powered by electric (battery powered), diesel, gasoline, or propane. For internal combustion forklifts, the engine is typically located toward the rear of the forklift, under the seat. Propane powered forklifts often have the tank mounted externally for easier access.
The back of the forklift provides the operator with another surface against which to support the load and is attached to the cart. It helps prevent the load from sliding back toward the forklift operator during lifting and traveling conditions. The forklift backrest also helps protect the forklift mast and mast components from being damaged by the load.
It is important to use a load backrest that is designed for the forklift. It is also important never to disassemble the seatback before operating the forklift for your own safety as well as the well-being of the forklift.
Knowing the general parts that forklifts have helps you understand how they work correctly.
This is an electric machine that performs the movement and the turning and lifting maneuvers by retracting the mast, thereby moving it towards the machine’s center of gravity.
Thanks to this feature, they outperform counterbalanced trucks in:
– They weigh less than them.
– They can work in narrower maneuvering aisles (± 2,700 mm free).
– They get a better performance.
On the other hand, although the masts and forks are similar to those of the counterbalanced ones, to leave or take the pallet from the racking the machine is centered in front of the load unit and the mast moves outwards, which facilitates the maneuvers.
There are forklifts that can lift the load above 10 meters, being able to place assistive devices, such as cameras, to facilitate maneuvers at the highest levels. Due to all these advantages, they are currently the most used machines to work in warehouses.
There are two models of this type of forklift
Double bottom reach trucks
Retractable machines capable of working on double-deep racking are available on the market. In addition to having a movable mast, these models incorporate forks that also move, allowing access to the second-depth pallet.
These are a model of pallet truck where the driver or forklift is usually on top and the forklift claws are in the rear position and can transport from one to two pallets. In addition, the person in charge of said transport must also have a radio frequency device to compose the order.
The machines that have the capacity to lift the crew are also order picking trucks and not trilaterals. These are called high-level, so it can be differentiated between two models of order picking trucks, the high-level, which collect goods located at a height, and the low-level, which only work at ground level.
These are machines to work in narrow aisles (between 1,500 and 1,800 mm), thanks to which the storage capacity is considerably increased. These forklifts can reach load lifting heights in excess of 14 m.
This model can have the head that supports the fork that is capable of turning on itself, being able to pick up and leave loads on one side or the other of the aisle and also from the front. They are also capable of leaving the pallets directly on the ground.
Or you can also have the forks are telescopic and are mounted on what is called a cradle. Unlike the trilateral machines, these machines cannot leave the pallets on the ground, nor can they position them from the front, but they have an advantage over those that need an even narrower aisle and can achieve a greater number of cycles.
It is the simplest and most widely used medium in modern warehouses. In its two versions, hand pallet truck and electric pallet truck, they are transport equipment, not lifting equipment.
In modern warehouses, the simplest and most widely used means is the pallet truck. It is a transport equipment, not a lifting one, that is handled manually in most cases.
These machines are very versatile, since they can be used to carry out multiple tasks such as loading and unloading trucks, moving pallets and containers over short distances, or serving as auxiliary means of support in picking operations. They are also used as auxiliary elements for the supply of intake areas, which are positions within the warehouse where the loading units are placed so that forklifts of all kinds, whether they are counterbalanced, retractable, three-sided and even stacker cranes, collect and transfer them. place in the corresponding holes.
The pallet truck can be manual or electric. The manuals are handled by an operator who must go on foot, while in the electric ones, the person can go on foot or mount them, depending on the model. They can be a good choice for small to mid-sized warehouses or construction sites. Here are the four simple steps for using a manual pallet jack.
This is used to help lift, move and stack palletized goods that are too heavy to lift manually. The main purpose of a pallet stacker is to load and unload pallets into trucks and transfer pallets from one location to another within a warehouse or storage space. Most pallet stackers are constructed of heavy-duty materials to withstand extreme weights and heavy daily use.
If you are thinking of purchasing a stacker, these machines will be perfect for small and large items that need to be moved around a warehouse or any location for approximately 5 hours a day.
They are suitable for indoor use due to their small wheels. However, it is recommended that it only be used on flat concrete floors.
This can be a manual pallet stacker that is manually operated and hydraulically operated to facilitate the task of lifting heavy pallets. Or they can be electric; they facilitate the stacking of heavier pallets when lifting weights of up to five tons.
These are those forklifts that work wonderfully in closed and small spaces since they do not disturb since they do not generate any type of noise. As its name indicates, these devices do not work with combustion, but are powered by a large lead battery that can last up to eight consecutive hours without a break. They are very functional and preferred by many.
They are ideal for interiors. Some applications are food handling, chemical products (EE), inside refrigerators or freezers (Cold Storage) Suita These electric powered forklifts are ideal for loading and unloading tractor-trailers, handling pallets, and a host of other applications in industries ranging from food storage and retail to factory and general warehousing.
Because they are battery-electric, Class I forklifts are much quieter and create no emissions, making them a popular choice for indoor applications. Class I forklift batteries also function as part of the counterweight to help maintain lift capacity
These are internal transport solutions that are used to support just-in-time and just-in-sequence production processes.
This equipment moves around the plant by towing different trolleys or gantry cars behind it that can be individually loaded according to the requirements and demands within the plant. Due to limited space for keeping stock on production lines, materials are delivered to the assembly line without the need to use forklifts for full pallets or partial pallets with multiple routes.
The advantages of this equipment are:
-Supply and disposal of materials simultaneously; no empty runs.
-Faster operation than with small forklifts.
-Different materials can be transported at the same time.
-Optimized equipment cost and labor.
-Optimized virtual clutch and drawbar system provides excellent train stability.
The engines of these forklifts run on gasoline, LPG or diesel. Unlike electric ones, these equipment are quickly replenished, they don’t have to wait for the battery to charge. The LP Gas-based forklift can be used in closed environments due to its low level of contamination.
It has an interior seat for the operator. According to the model, they support a load capacity of up to 3 tons. Its pneumatic wheels offer cost-saving productivity-enhancing features, including long-life warranties on essential components.
This model is ideal for indoor and outdoor heavy-duty applications, they provide the durability and versatility you need to get the job done, best suited for the paper, steel, machinery and fabricated metal industries.
Some of its benefits are:
-Customizable for the application
-Ergonomic features
-Simple serviceability
-Attachment options
This versatile forklift is specifically designed for indoor use. As its name implies, it works by combustion (gas / gasoline) or diesel is used to lift loads of different shapes or sizes. Collection, storage, warehousing and storage, and is especially suitable for applications such as primary metal products, stones, clay, glass and concrete, as well as industrial and commercial machinery.
The advantages of this equipment are:
-Less downtime
-Low cost of operation
-Operator comfort
-Higher productivity
-Performance options
A big advantage is that its tires are not easily punctured by debris found in the workplace, such as pieces of metal or nails. Excellent durability for external environments, such as recycling centers or logging, due to its ability to adapt in difficult terrain. They are generally more expensive than inflated tires, but the smooth option has long life and maximum productivity on tough job sites.
This equipment is capable of lifting all types of loads and they are generally found in seaports, airports and large warehouses where the transfer of heavy containers twice their size is required.
For this, it has a lifting platform in the front, made up of two high-resistance steel forks that go up and down two masts, using roller chains.
This machine is capable of lifting 40,000 pounds (18 tons) with the base retracted and up to 60,000 pounds (28 tons) with the base removed, and is equipped with a removable hydraulic boom, coupled to a three-speed electronic transmission. forward and three backward.
In order not to unbalance the machine with the load, a counterweight is located at the rear end of the chassis so that it can lift objects as huge as a 12-meter container.
The cab features an independent suspension seat, a depth and tilt adjustable steering column, and a video camera to monitor the rear.
The command post includes a digital control screen to monitor all functions and reports through a sensor the load capacity and automatically adjusts the hydraulic flow according to the demand that is required.
The High-Capacity Internal Combustion Damping Large Forklift is a gigantic indoor machine. Ideal for automotive environments and for moving steel within manufacturing facilities, it gives you the ability to lift massive weights without difficulty. And with one of the leading engines in its class, the High-Capacity Large Forklift is as reliable as it is strong.
The High-Capacity cushion Forklift is the best option when it comes to versatility in the warehouse or manufacturing facility. If you are needing to lift large pallets full of heavy components, the High-Capacity cushion has you covered with its ability to lift up to 22,000 lbs. You’ll have those pallets of metal moving in no time. Have a paper plant with larger than normal rolls? The High-Capacity Cushion can come with a roll clamp to make those operations a cinch.
All these heavy machinery equipment have high quality standards, and various characteristics that make them ideal for each function. If you are interested in obtaining advice on the use of these forklifts, do not hesitate to contact us, we will gladly help you.
Pallet jacks are some of the most essential tools found in warehouses and construction sites. Cheaper and easier to operate than forklifts, and safer than manual labor, pallet jacks are used for transporting small loads for short distances.
These tools come in two variations: manual pallet jacks and electric pallet jacks. Both can be good options depending on the size and scope of the project. If you’re thinking about investing in one of these tools but are wondering how to use a pallet jack, take a look at the step-by-step instructions below.
How to Operate a Manual Pallet Jack
Manual pallet jacks are simpler and more affordable than electric pallet jacks, and also require less upkeep. They can be a good choice for small to mid-sized warehouses or construction sites. Here are the four simple steps for using a manual pallet jack.
Locate Release Lever
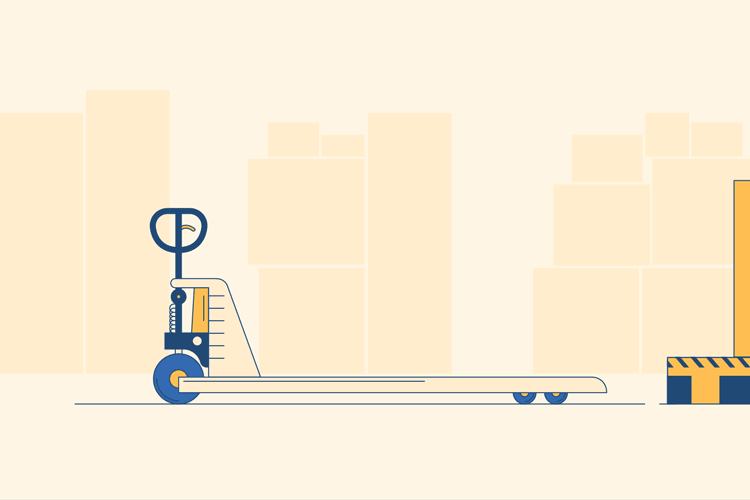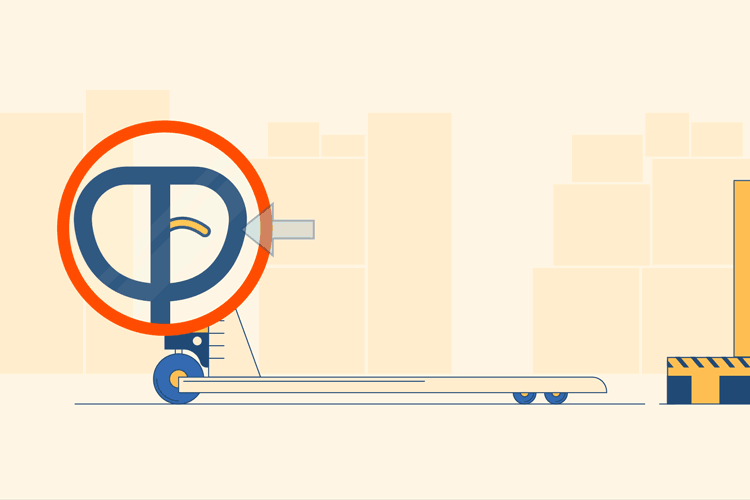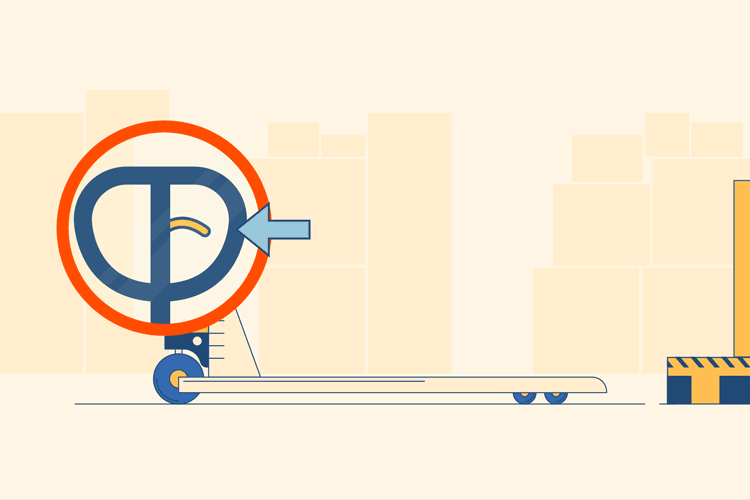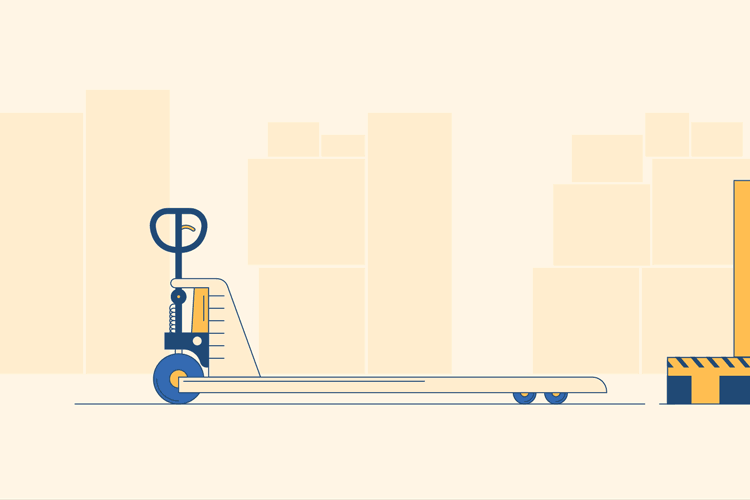
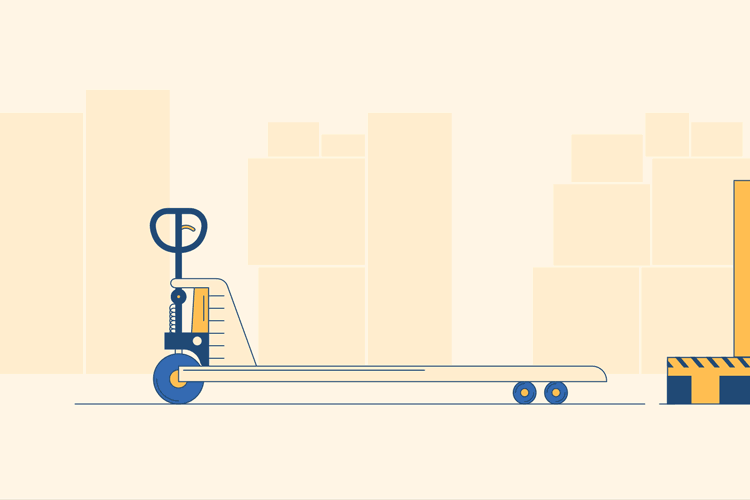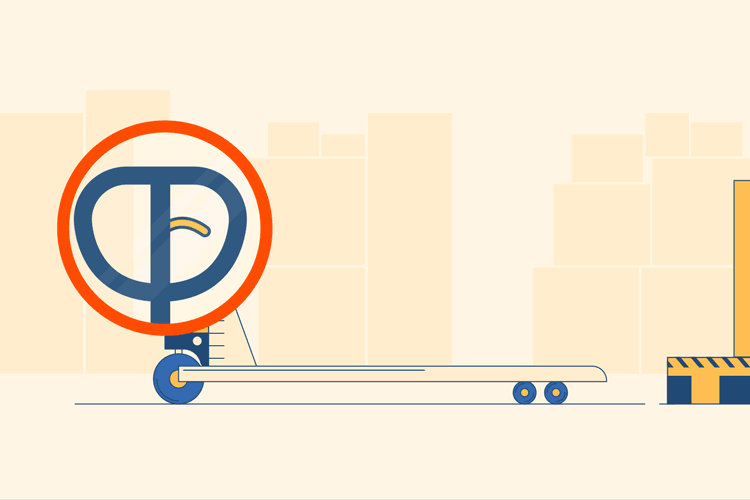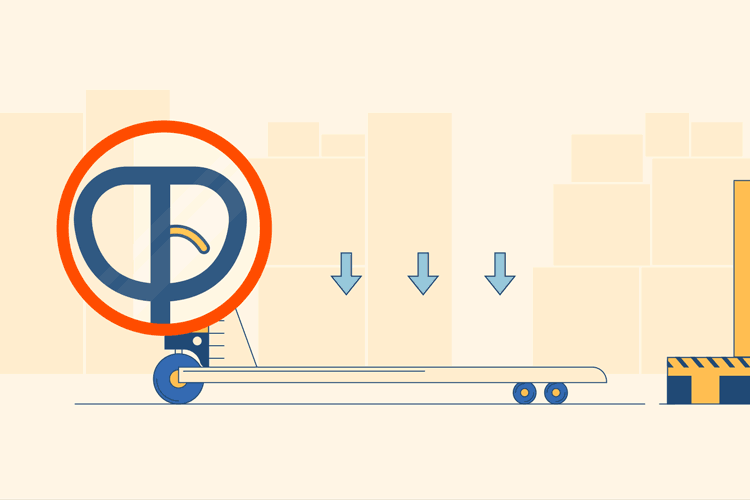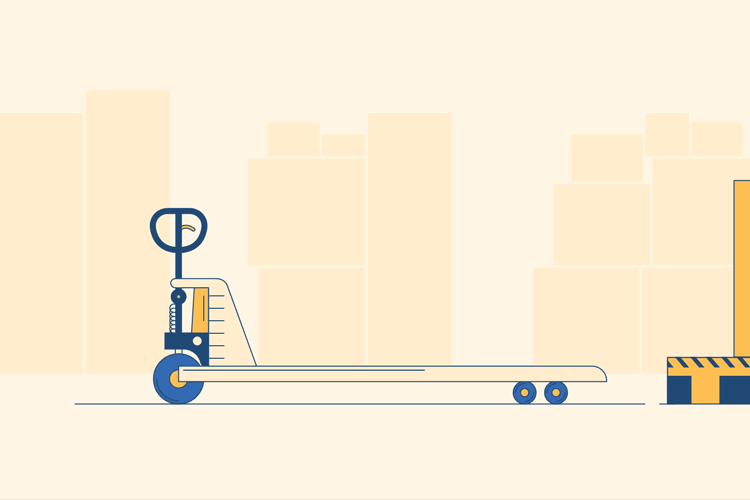
Stand behind the pallet jack with your hands on the metal steering handle, toward the prongs, which are facing outward. The prongs are the two horizontal pieces of metal which will actually lift the pallets. Locate the plastic release lever on the handle; this is usually found attached to the center bar. It may be a different color in order to make it stand out, but if not it should still be obvious.
Move to the Pallet and Press the Lever
Move the pallet jack to whatever you want to move and engage the lever to lower the prongs.
Next, push the pallet jack over to the pallet you would like to move. Press the release lever up and inward to lower the prongs to about one-inch off of the ground. If the prongs are already lowered, they will not move when you press the lever.
Slide the Prongs Under the Pallet to Load
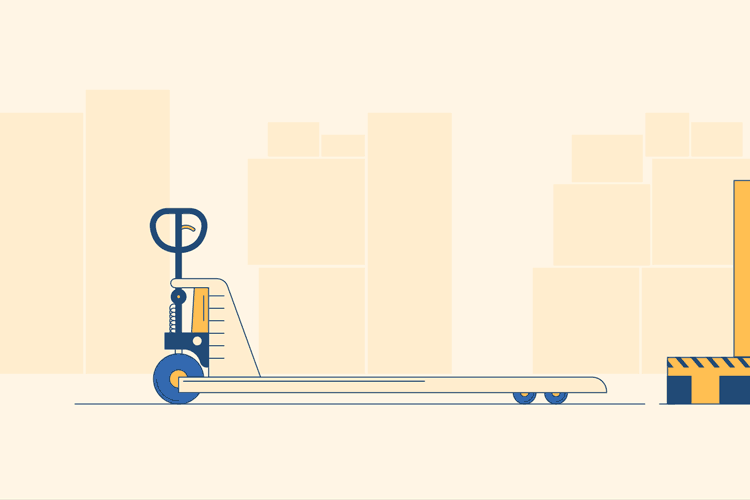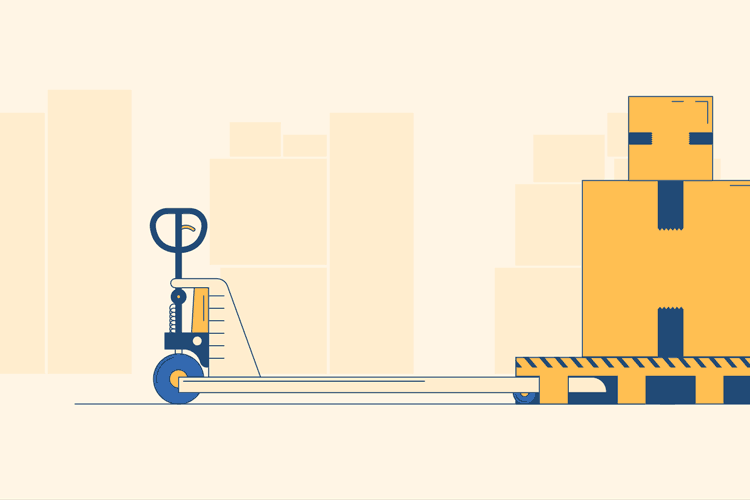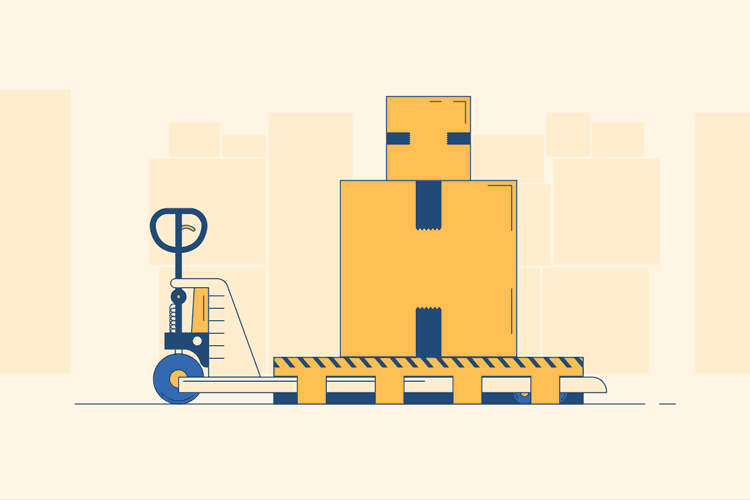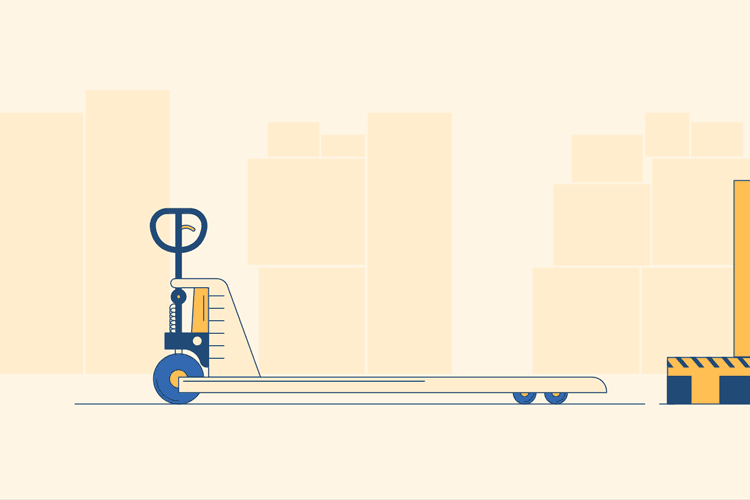
Once the prongs have been completely lowered, you can slide them underneath the pallet you would like to move. If they are still too high to easily slide under the pallet, they may not be lowered all the way and you should press the release lever again. Make sure you push the prongs all the way through the underside of the pallet so that the wheels are resting on the floor and not on any part of the pallet.
Jack Up the Pallet
Animation showing the pallet being lifted due to pushing down the handle.
Once the prongs are positioned underneath the pallet, pull the metal handle and the entire center bar toward you at an angle. You should feel some resistance and notice the prongs slowly lift up the pallet. Repeat this several times so that the prongs are far enough off the floor not to drag.
Move the pallet jack to whatever you want to move and engage the lever to lower the prongs.
Next, push the pallet jack over to the pallet you would like to move. Press the release lever up and inward to lower the prongs to about one-inch off of the ground. If the prongs are already lowered, they will not move when you press the lever.
Slide the Prongs Under the Pallet to Load
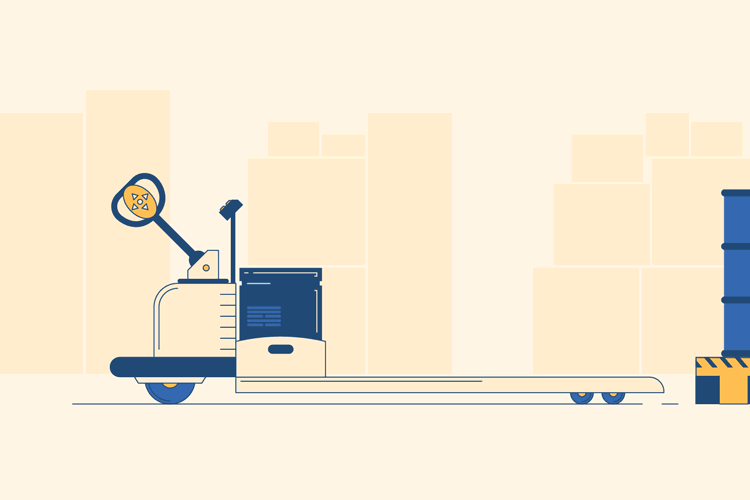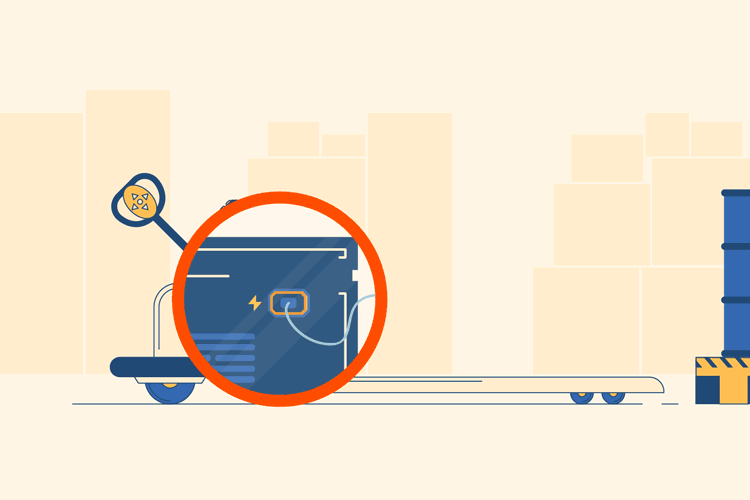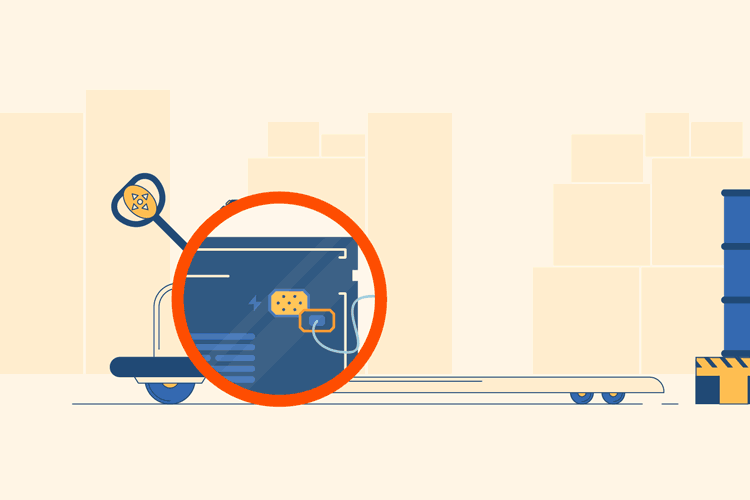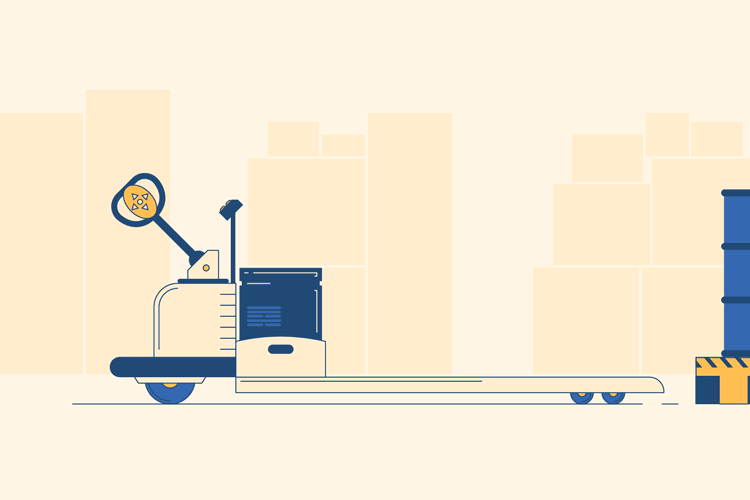
Unplug the electric pallet jack’s plug when you are using it.
Your first step for operating an electric pallet jack is to unplug the charging cord and store it away inside the machine. Because they run on electricity, electric power jacks need to be plugged in and charged when they are not in use. There is usually an obvious location to insert and store the length of the cord.
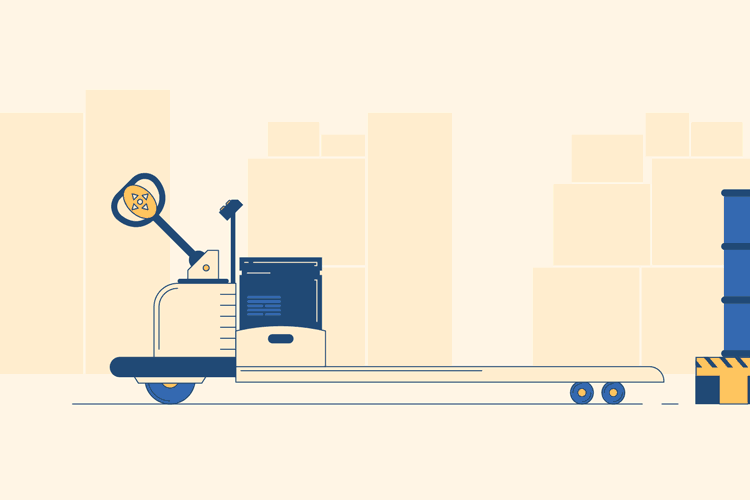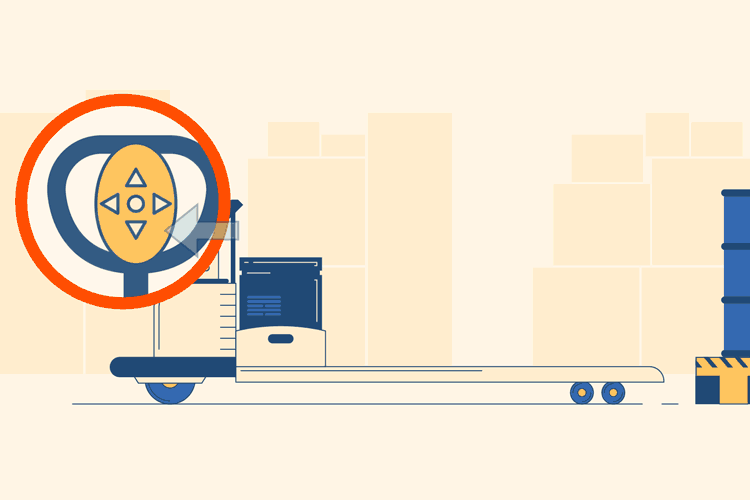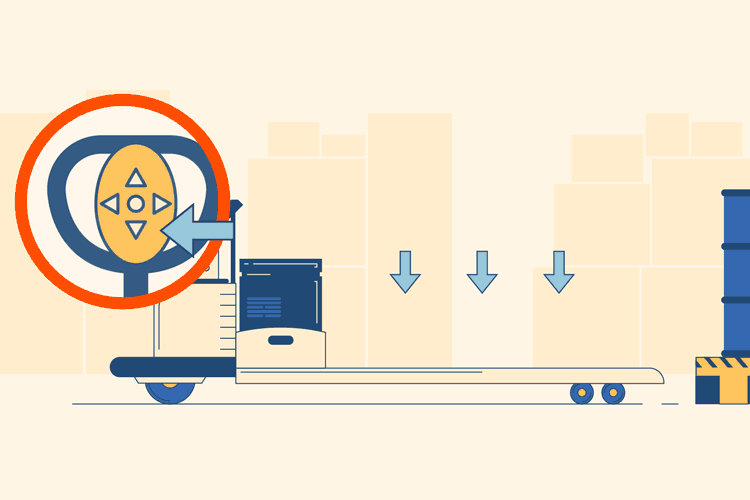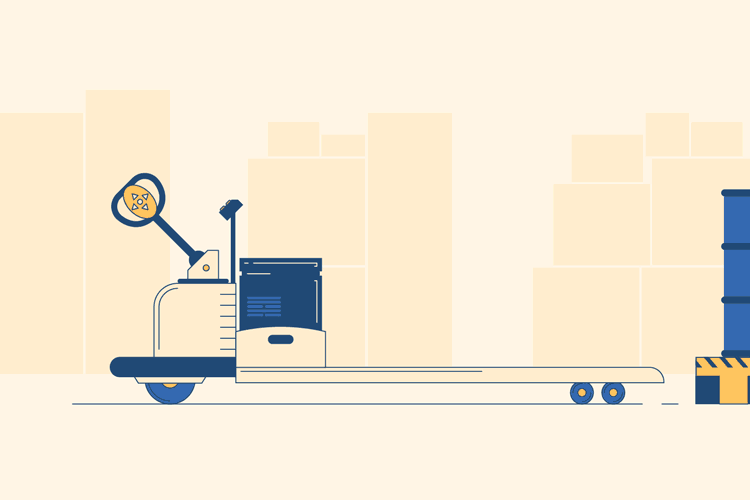
Identify the Controls and Lower Prongs
On the handle of the pallet jack, there should be buttons to control the direction of movement. Push the “down” button to lower the prongs toward the floor. Again, these should be about one to two inches from the ground.
Load the Pallet
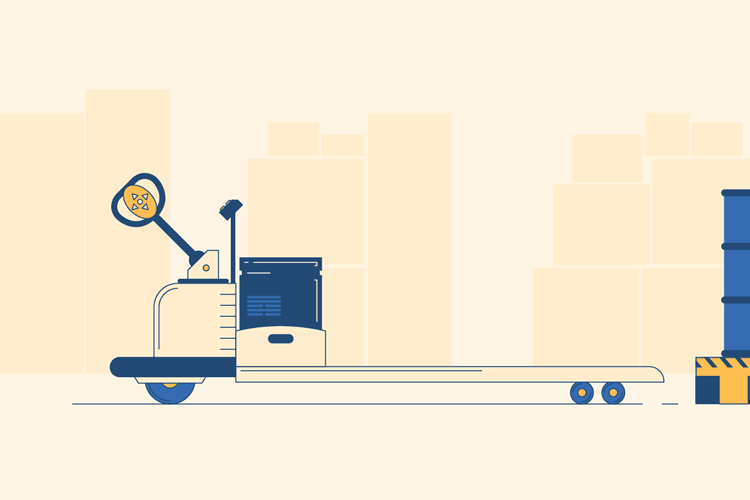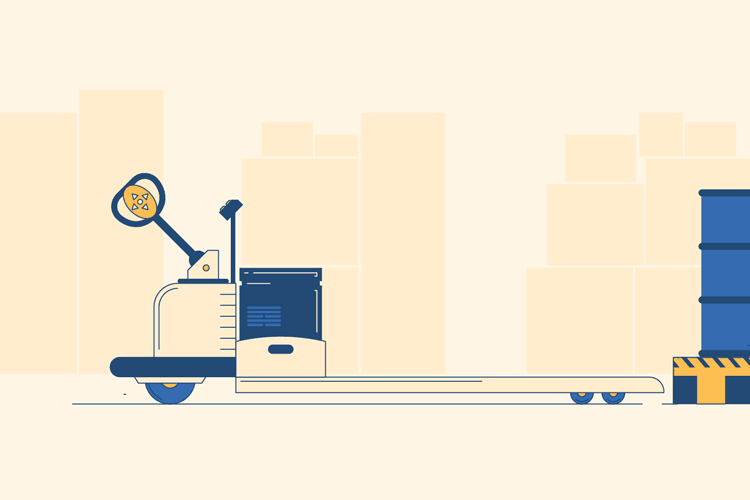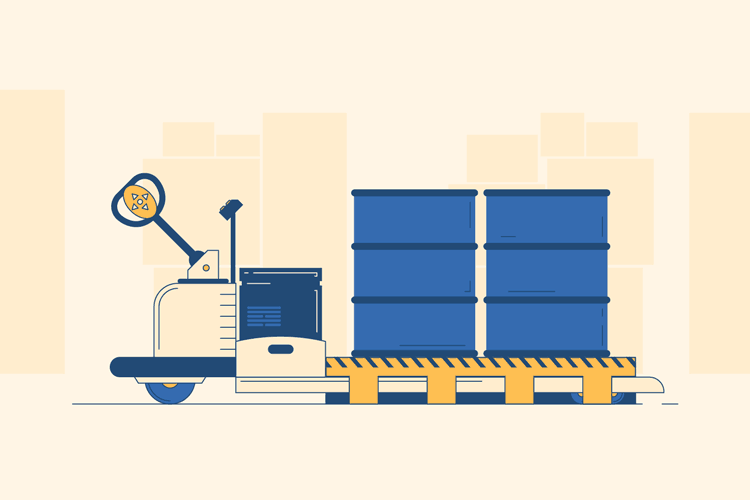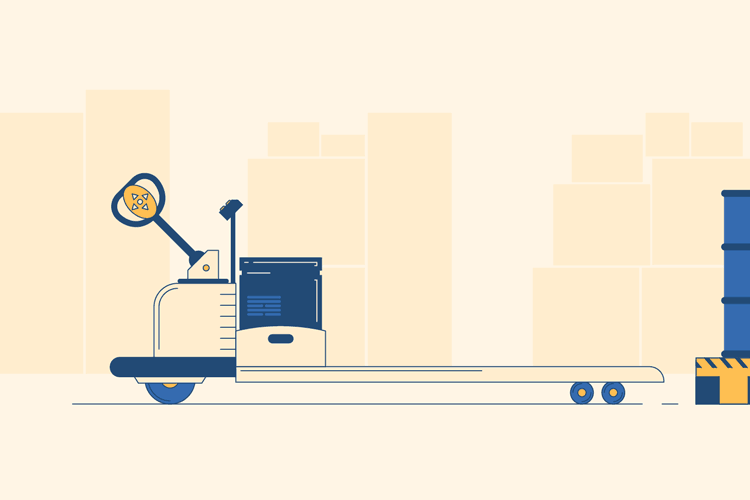
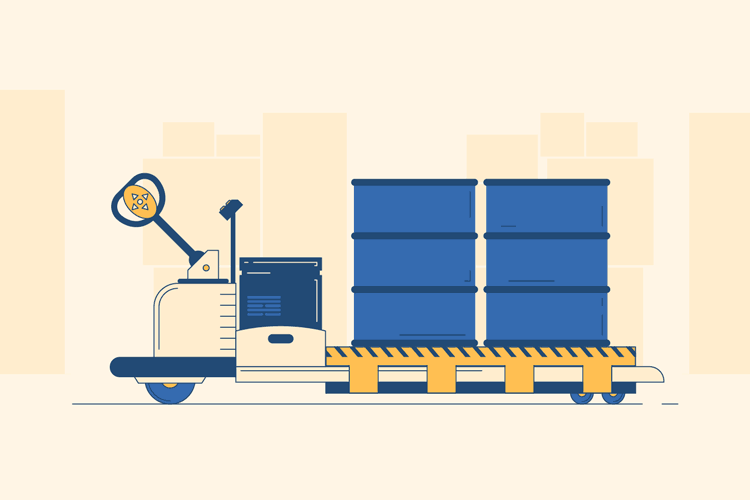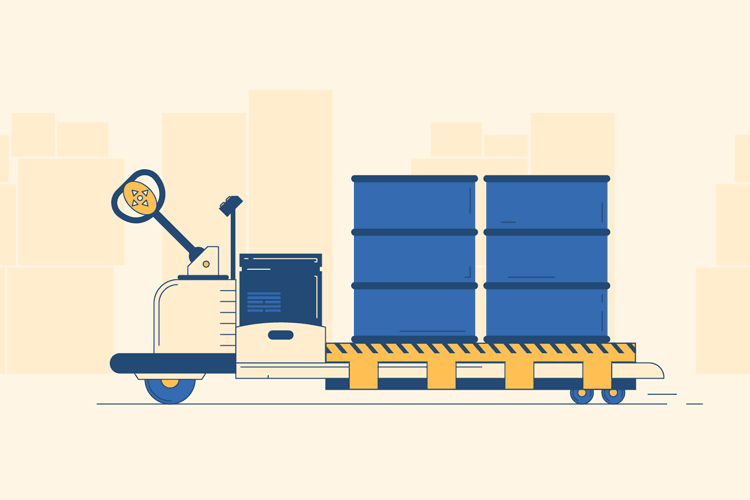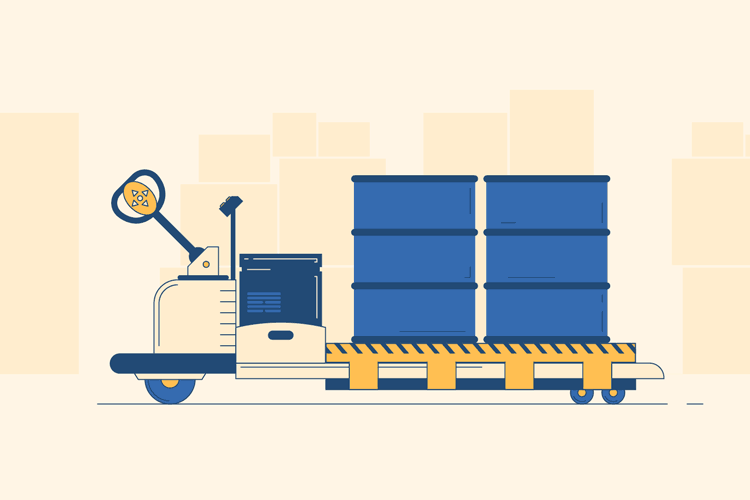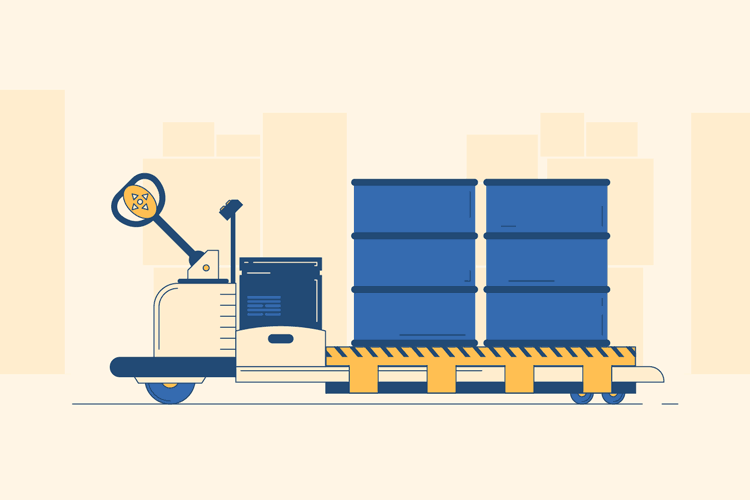
Next, use the controls to move the pallet jack to your destination. Once you arrive in front of your pallet, use the buttons to maneuver the prongs underneath and all the way through the pallet. Then, press the “up” button to lift the pallet and prongs off the ground.
Use the Control Buttons to Move
Once you have your pallet securely loaded, you can use the control buttons to move to your destination. When you arrive, again press the “down” button to lower the prongs and pallet to the floor.
Charge the Electric Pallet Jack
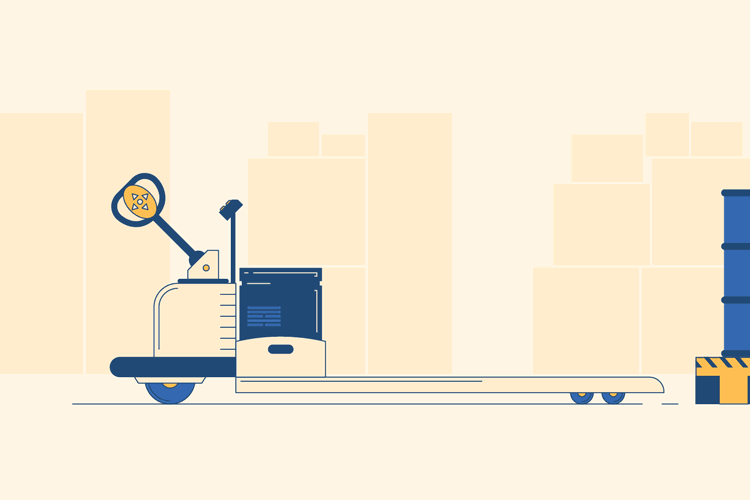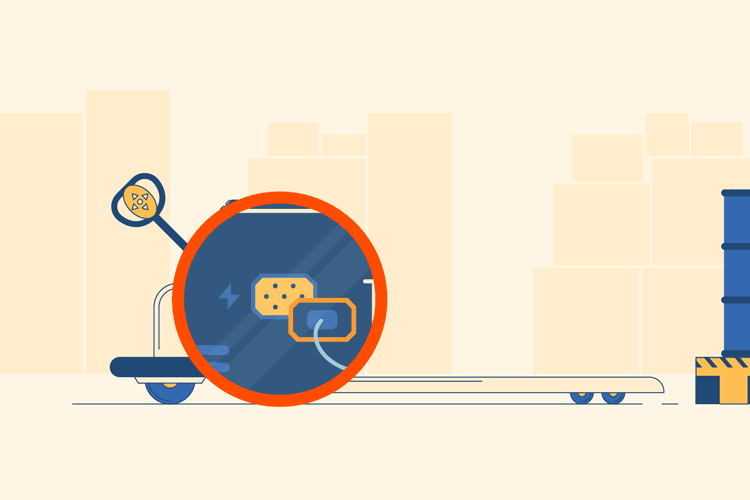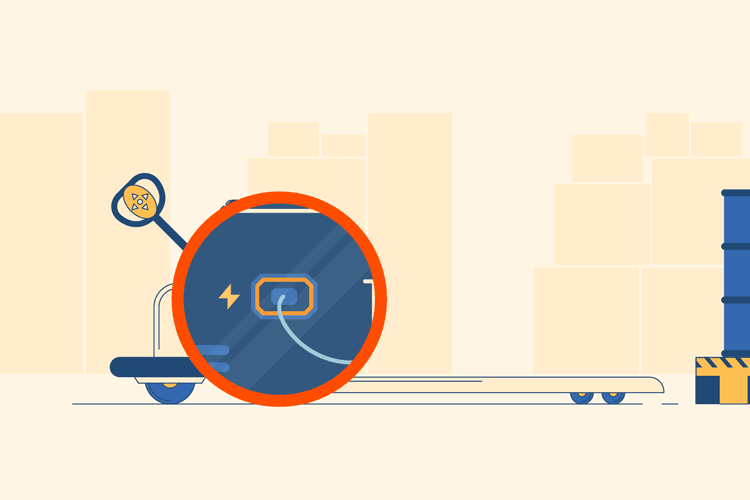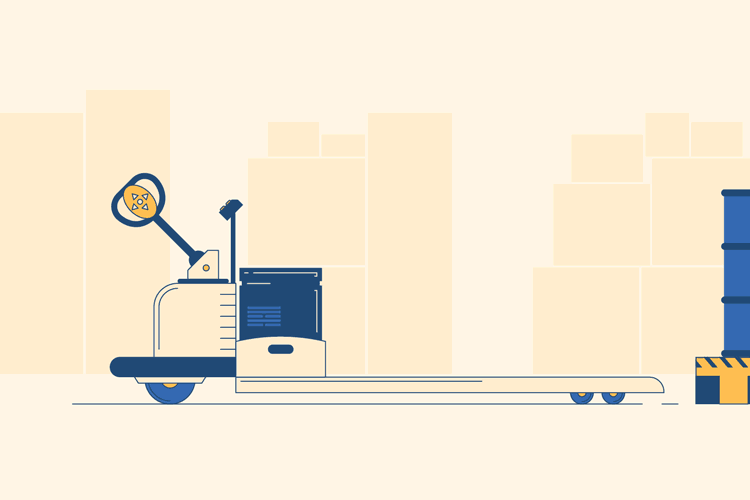
When you are done, put the electric pallet jack back as you found it. You will need to pull out the charging cord from its storage area in the machine, and plug it back in so that the electric pallet jack will be ready for use the next time it is needed.
You can push and pull a pallet jack, depending on how you need to maneuver it. However, humans are able to push much more weight than they can pull and excessive pulling can result in injury.
Though they are relatively simple machines, pallet jacks can still be dangerous if the proper safety precautions aren’t taken.
One of the most important steps before operating a pallet jack is to take a look and make sure everything appears ready and functional. You will want to look for things such as loose prongs, unbalanced wheels, or charging cords that aren’t stowed properly.
Though it may seem like a pain, it’s worth it to take the extra couple minutes to make sure you don’t accidentally drop your pallet due to a faulty pallet jack.
The second step is to make sure that the route you will be taking to the pallet and your drop-off point is clear of all obstacles. Look for stray construction materials and electric cords, and take note of the ground surface. If the ground is too bumpy, it may be best to find another route.
This step is especially important if you are working on a site that non-workers can easily access, such as a retail warehouse or home renovation. Make sure that the pallet jacks are kept in an area that is not easily accessible by customers or civilians, and that the machines are kept out of the way for other workers that need to move around the site.
In order to comply with OSHA safety regulations, operators of both manual and electric pallet jacks should complete a certification course. These are often supplied by individual employers, and there are online certifications available as well.
Most manual and electric pallet jacks can handle up to 3,500 kg, or 7,700 lbs. This depends on the size and model that you are using, as there are some that are made to handle larger weights. Consult the instructions for the specific model you plan to use for exact measurements.
Whether you decide to go with a manual pallet jack or an electric pallet jack, either choice will make your next construction project so much easier, as you won’t be stuck doing all of the heavy-lifting on your own. Take a look at our selection of pallet jack rentals to decide which would be the best fit for you.
Especially for more powerful machines like electric pallet jacks, you will want to make sure that only authorized personnel are able to operate. You could keep access restricted with a security code that must be entered in order to use the machine, or with something as simple as a desk with a sign-in sheet which will allow you to keep track of who is using each one.
